SD goes undercover with Embedded SD
Last updated Sep 11, 2008 — 3124 views You’ve heard of SD, miniSD, and microSD cards. Now, get ready for Embedded SD — a new standard set for release this November by the SD Card Association.
You’ve heard of SD, miniSD, and microSD cards. Now, get ready for Embedded SD — a new standard set for release this November by the SD Card Association.
The group’s new Embedded SD specification will define the mechanical, electrical, and functional specifications of an embedded version of the popular SD card technology.
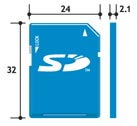
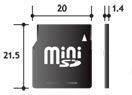
Embedded SD is largely compatible with SD, miniSD, and microSD cards (left to right)
Embedded SD form-factor
 According to SD Card Association spokesman Rex Sabio, Embedded SD memory and I/O modules will have form-factors similar to that of IC BGA packages (shown at the right).
According to SD Card Association spokesman Rex Sabio, Embedded SD memory and I/O modules will have form-factors similar to that of IC BGA packages (shown at the right).
The chip-like modules will come in several sizes ranging from 11.5 x 13mm to 16 x 20mm — roughly the size of microSD and miniSD cards, respectively — but with a consistent BGA pinout. Regardless of horizontal dimensions, the modules have a maximum height spec of 1.4mm, Sabio said.
Sabio also hinted that device-makers would be able to accommodate a range of Embedded SD module sizes within a single device circuit-board design.
Although different mechanically, Embedded SD shares a common host interface with its removable siblings — SD, miniSD, and microSD cards — pictured above. Thus, all four types of SD devices should work with the same electrical interfaces and software drivers, easing the incorporation of Embedded SD into next-generation mobile phones and consumer gadgets.
Using the new standard, host devices will be capable of supporting up to 32GB of on-board memory, supplied by Embedded SD devices, along with up to 32GB of removable memory, supplied by SD, miniSD, or microSD cards, according to the SD Card Association.
Summary of Embedded SD features
Here’s a list of claimed features of the soon-to-be-released Embedded SD standard:
- Compatible with SDHC (SD 2.00), ensuring seamless migration from current SD designs
- Supports both 3.3V and 1.8V power supplies, for both flash and I/O devices
- Provides boot from Embedded SD capability
- Flexible partition mechanism allows multiple physical partitions for boot code, OS, applications, multimedia, etc.
- Protection mechanism — each physical partition can be configured with different read and write/erase protection modes
- Data robustness — Optional configuration of each physical partition of the Embedded SD device, including full immunity to power failure and protection of critical data (boot code, operator data, etc.).
- Power-saving sleep mode permits customizing power needs and reducing power consumption
Further details should emerge on the SD Card Association‘s website later this year.


